Why Blood Clots Occur?
When our skin is cut, our body forms blood clots in order to prevent the loss of blood. But it also thins the blood and contains the clot to improve blood flow to repair the injury. This helps continue the supply of essential nutrients to organs and tissues. When an infection or inflammation occurs, this clotting cascade also begins as an immune response to protect the body. Our body is constantly trying to maintain this delicate balance between promoting blood clots and thinning the blood. However, in chronic inflammation or prolonged infection, this balance sometimes tilts towards too much coagulation leading to sticky blood. (Ref: 1)
Blood Clots and COVID-19
Covid-19 is a viral infection which causes inflammation and the production of blood clots at a later stage. In addition, it is well documented that certain Covid injection can also lead to blood clots as a result of platelet activation during the production of antibodies.
Dr. Jonathan Liu, Professor of Chinese Medicine at Georgian College in Canada, wrote an article at the Epoch Times. He discussed how blood clots are treated. He cited an investigation of large-scale surveys in England and Ireland which revealed that many patients developed venous thrombosis during long COVID. Venous thrombosis is blood clotting in the veins often as a result of slow blood flow, poor drainage and a hyper coagulable state. (Ref:2)
Treatment for Blood Clots
Pharmaceutical options for blood clots include anticoagulant therapy, anti-platelet therapy, thrombolytic therapy and fibrinogen-lowering therapy. These may offer speedy help. However, care must be taken to monitor the risk of bleeding.
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) treatment for blood clots does not target only the blood clots but also the environment that result in the blood clots. It expands blood vessels, reduces inflammation, reduces blood pressure and blood viscosity (‘stickiness’) and blood lipids. It stops platelet clumping and improves microcirculation in order to prevent and eliminate thrombosis. (Ref: 2) It achieves this by combining Qi (life force), Blood tonics and Blood invigorators. However, it is essential to seek professional advice instead of mixing your own herbs as an overdose can also cause bleeding.
How Chinese Medicine Works
Chinese medicine formulas involve a number of Chinese medicinals decocted together to achieve a synergistic effect. Some work to invigorate the blood while others work to promote movement. Still others work to harmonise all herbs to reduce toxicity. Here are some examples of herbs used together to improve blood clotting (Ref: 3).
Blood invigorators:
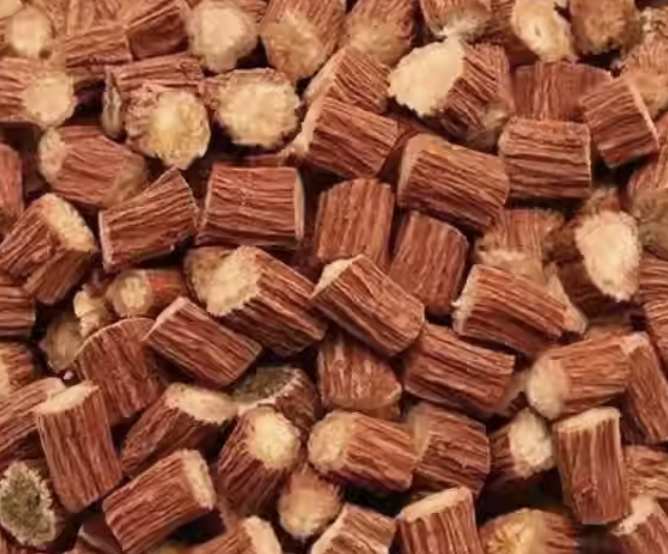

Dan Shen, radix Salvia Miltiorrhizae
It dilates coronary arteries and peripheral vessels and reduces blood pressure in the short term in animal studies. It improves cardiological outcomes of patients with angina pectoris. It lowers the serum cholesterol of some patients. It has been shown in studies to have a sedative effect and reduces blood sugars.
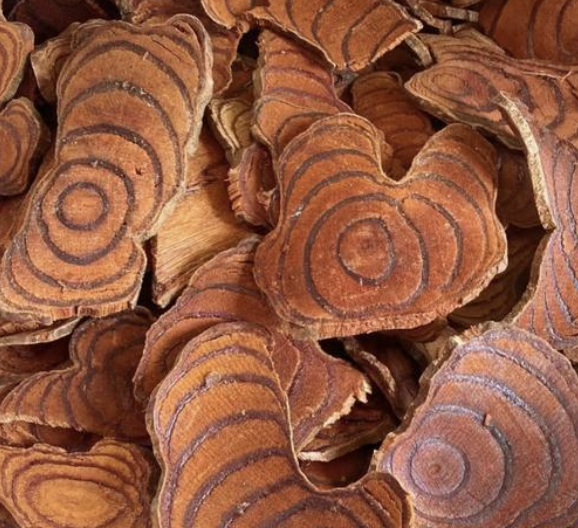

Ji Xue Teng, Radix et Caulis Jixueteng
Animal studies have shown that Ji Xue Teng lowers blood pressure, reduces inflammation and calms the nervous system.
Qi Tonics:
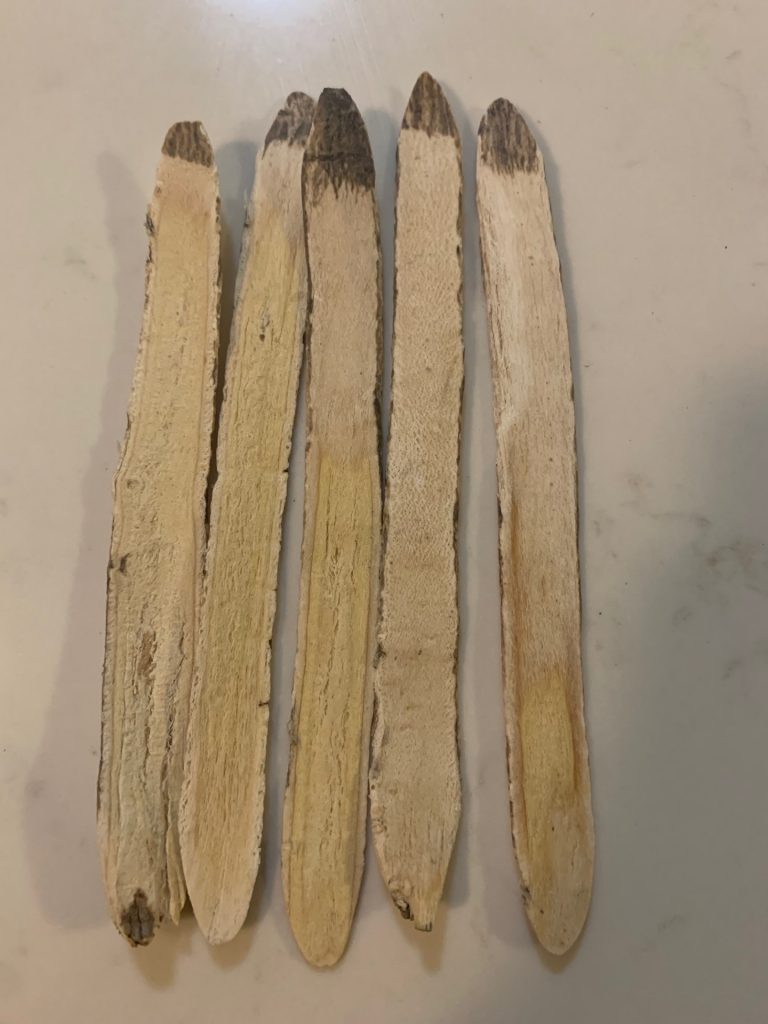

Huang Qi, Astragali radix
Animal experiments have shown that it promotes blood cells formation & stimulates the immune system. It also dilates peripheral blood vessels, protects the liver and has antibiotic, analgesic and sedative properties.
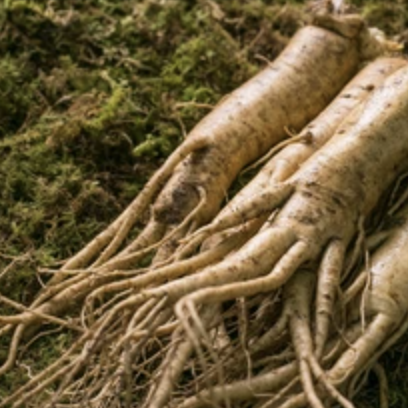

Ren Shen or Radix Ginseng
It increases endurance (adaptogen), stimulates the immune system and improves energy and memory.
There is an intricate balance in dosage among Chinese medicinals. It is essential to seek advice from an experienced practitioner before mixing and matching different medicinals to avoid unwanted side effects.
References
- Hypercoagulability: ‘Sticky’ Blood is Present in Nearly all Chronically Ill Patients, Dr. Ann Corson, Epoch Health, https://www.theepochtimes.com/health/ask-a-doctor-what-is-hypercoagulability_4535844.html?utm_campaign=socialshare_email, 2022
- How To Reduce Blood Clots After COVID 19, Dr. Jonathan Liu, Professor of Chinese Medicine at Georgian College, Canada, 2022
- A Materia Medica for Chinese Medicine, Carl-Hermann Hempen, Toni Fischer, Churchill Livingstone, 2009



Leave a Reply